PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
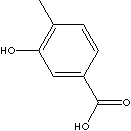
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY
APPLICATIONS
Benzoic acid derivatives substituted by hydroxy group or ether containing oxygen atom have active bacteriostatic and fragrant properties. They are typically used in pharmaceutical and perfumery industry. The destructive metabolic property of oxygen containing benzoic acid derivatives such as protocatechuic acid (3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid) and veratric acid (3,4-dimethoxybenzoic acid) is used in the application for pharmaceuticals. Protocatechuic acid is a catabolite of epinephrine. Prazosin, a peripheral vasodilator and antihypertensive, is also an example of the applicaion of veratric acid. Hydroxy and ether substituted benzoic acids feature analogue metabolite of aspirin (acetylsalicylic Acid). They are used as intermediates for pharmaceuticals (especially for antipyetic anlgesic, antirheumatism) and other organic synthesis. They are used as matrix for ionization of peptides, proteins and carbohydrates.
APPEARANCE
MELTING POINT
207 - 211 C